Talking to teens about mental health can feel overwhelming, but these conversations are more important than ever. With rising rates of anxiety, depression, and stress among adolescents, it’s essential that parents and educators create safe spaces where teens feel heard, supported, and empowered to seek help when needed. Here’s how to open the door to meaningful dialogue and support their mental well-being.
Start Early and Normalize the Conversation
Mental health shouldn’t be a taboo topic saved for crisis moments. Begin conversations early by talking openly about emotions, stress, and coping strategies in everyday situations. Normalize mental health the same way you would physical health—acknowledging that everyone experiences emotional ups and downs, and it’s okay to ask for help.
Create a Safe, Nonjudgmental Space
Teens are highly sensitive to judgment. Approach conversations with empathy and without jumping to conclusions. Let them know you’re there to listen, not to lecture. Simple phrases like, “I’m here for you” or “It’s okay to feel what you’re feeling” can go a long way toward building trust.
Listen More Than You Speak
When a teen opens up, resist the urge to immediately offer advice or solutions. Instead, focus on listening fully. Ask open-ended questions like, “Can you tell me more about how you’re feeling?” or “What do you think would help you right now?” Listening without interruption validates their experiences and shows that you value their voice.
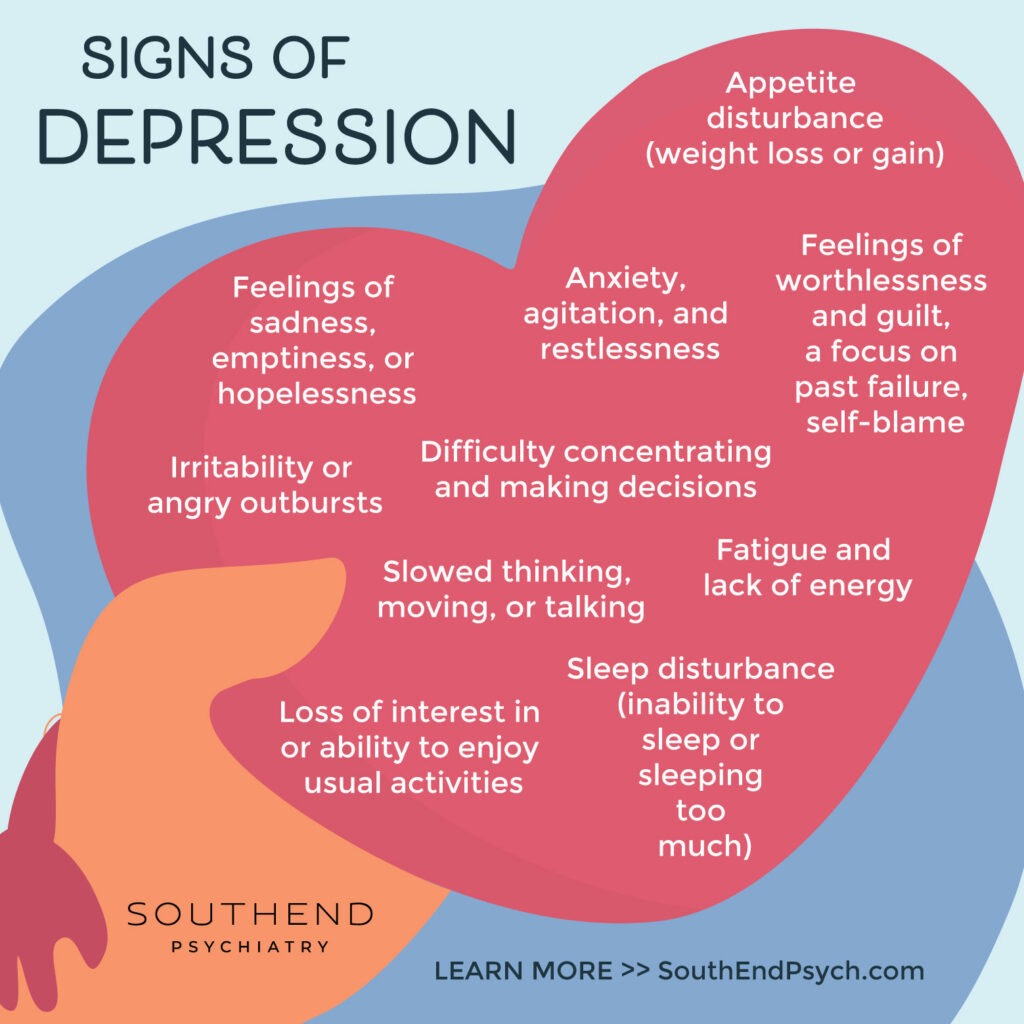
Watch for Subtle Signs
Teens aren’t always direct about what they’re experiencing. Changes in mood, sleep patterns, academic performance, or social habits can all be early signs of mental health struggles. Pay attention to these cues, and approach them gently, without accusation. A simple “I’ve noticed you seem a little different lately—want to talk about it?” can open a door.
Use Language They Relate To
Avoid clinical jargon or labels that might feel intimidating. Instead of asking, “Are you depressed?” try saying, “Have you been feeling really down lately?” Speak in a way that feels natural, relatable, and free of stigma.
Empower, Don’t Shame
If a teen shares that they’re struggling, validate their courage in opening up. Focus on empowering them with coping tools and resources rather than shaming them for how they feel. Reinforce the message that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Involve Professional Help When Needed
Sometimes professional support is necessary—and that’s okay. Let teens know that therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists are there to help them build skills and strategies for managing life’s challenges, not to “fix” them. Normalize therapy as a healthy, proactive choice.
Educate Yourself
The more informed you are about mental health, the more confident you’ll feel talking about it. Learn about common teen mental health conditions, risk factors, and warning signs. This knowledge helps you approach conversations from a place of understanding, not fear.
Be Patient and Consistent
Building trust takes time. Even if a teen doesn’t open up right away, keep the door open. Check in regularly, and remind them you’re always available to listen—no matter what.
At Southend Psychiatry, we believe that open, supportive conversations about mental health can change lives. Whether you’re a parent, teacher, coach, or mentor, your willingness to talk—and to truly listen—can make a lasting difference for the teens in your life.
If you or your teen needs additional support, our compassionate team is here to help. Contact Southend Psychiatry today to learn more about our services.
Southend Psychiatry
Schedule your appointment today with one of our SouthEnd Psychiatry clinicians. Book your appointment online or call 1-800-632-7969 to get started today.